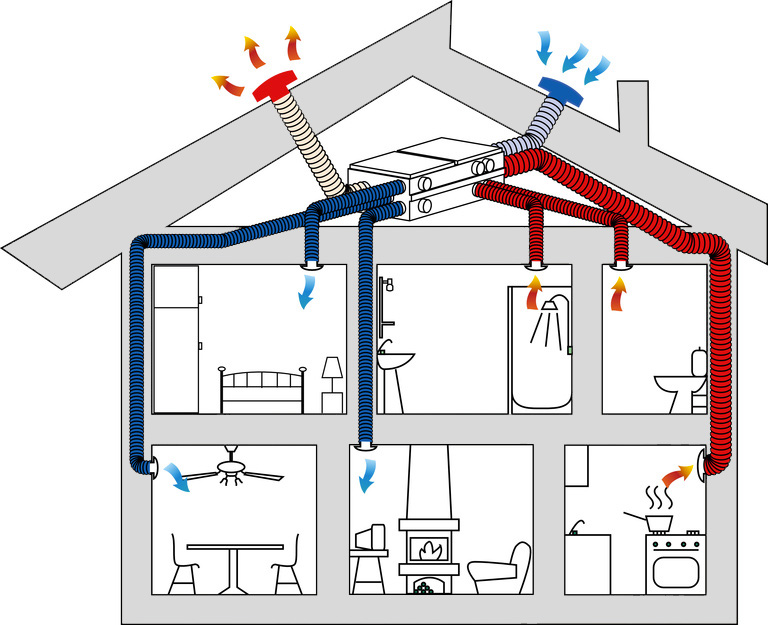
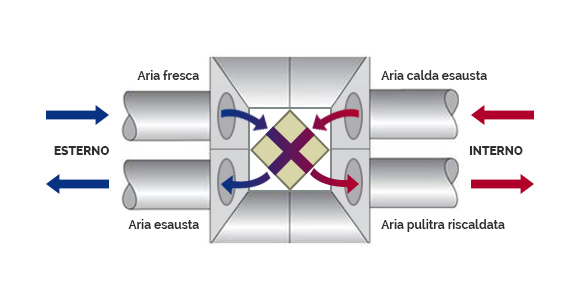
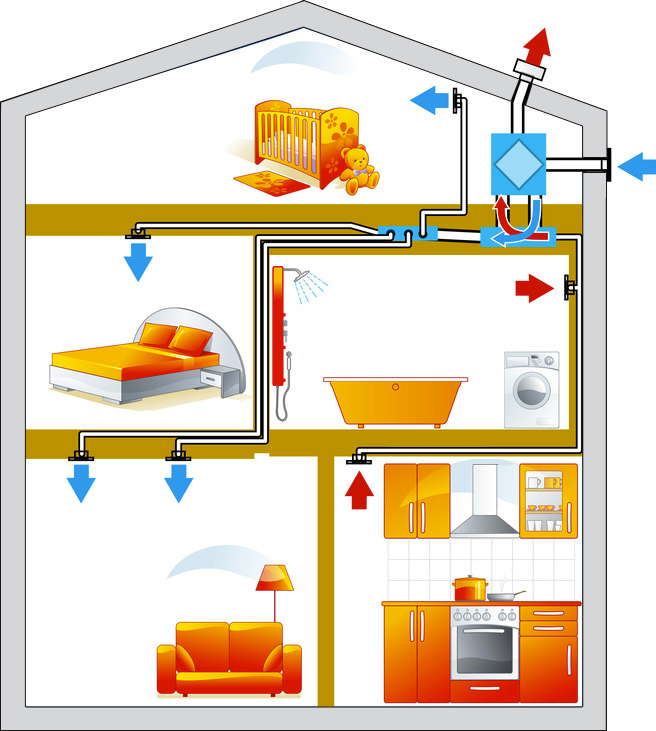
Problems with INDOOR air
Air inside buildings has a significantly higher level of pollution than outdoor air.

Co2

Moisture and mould
Bacteria and viruses

Radon

Cigarette smoking